OSHA Standards | A Closer Look At Workplace Safety Regulations
Do you want to construct a culture of safety from the ground up to real-time incident reporting and mobile-ready safety inspection? Firstly, you may understand the OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration Standards) to overcome workplace challenges.
An Overview of OSHA Standards and regulations
The imperative goal of OSHA regulations is to reduce health and safety hazards in the US by setting up safety guidelines and criteria. This organization imposes regulations on every small to medium-sized business, or even leading firms to ensure that their workplaces are safe and healthy as well as their employees receive training on OSHA health and safety standards before initiating their work. As per the National Safety Council estimation work-related injuries & fatalities will cost the U.S. economy $171 billion in 2019. Effective OSHA standards help reduce these costs significantly.
However, this comprehensive guide delves into the various facets of OSHA standards, their development, implementation, and their impact on workplace safety. Let’s get started!
The Purpose and Importance of OSHA Standards
OSHA standards serve a crucial role in safeguarding the health and well-being of workers across various industries. These regulations, crafted with meticulous care, ensure that workplaces are free from recognized hazards, thereby preventing countless injuries and illnesses. However, the importance of these standards cannot be overstated, as they embody a commitment to creating environments where every worker can thrive without compromising their safety. These standards serve multiple purposes:
Protecting Workers:
OSHA standards are designed to mitigate hazards that could lead to injury, illness, or fatality. They cover a wide range of potential dangers, from chemical exposure to machinery operation.
Legal adherence:
Adhering to OSHA standards is a legal requirement for employers. If they do not adhere with its regulations that will result in significant legal action and fines.
Enhancing Productivity:
Safe workplaces tend to have higher morale and productivity. Reduced injury rates lead to fewer disruptions and lower compensation costs.
Public Health:
By reducing workplace hazards, OSHA standards also contribute to broader public health by minimizing occupational illnesses that could affect families and communities.
Key Areas Covered by OSHA Standards
If you are wondering “What do OSHA standards cover”, here you read. It is a set of recommendations and instructions for businesses to reduce worker risk while performing job duties called an OSHA safety standard. It also includes regulations for materials and equipment. Workers have been protected from potentially dangerous situations and health concerns by following OSHA regulations. Four main industries comprise its organization.
General Industry:
It includes a wide range of businesses not classified under construction, agriculture, or maritime.
Construction:
In this OSHA industry standard participants focus on the unique risks present in the construction sector.
Maritime:
This OSHA standard addresses safety in the maritime industry, including shipyards and marine terminals.
Agriculture:
This OSHA adherence standard of safety covers the specific hazards associated with farming and related activities.
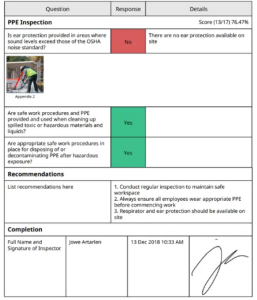
Source: OSHA Standards PDF report Template
The understanding of OSHA safety and health standards is highly important. You must learn different industry OSHA safety guidelines to build safe and sound workplaces for your employees.
General Industry Standards
General Industry standards (29 CFR Part 1910) apply to most worksites in the United States. Key standards include:
- It ensures that machinery is equipped with safety guards to protect operators from moving parts.
- Must limit noise levels to prevent hearing loss, requiring employers to implement hearing conservation programs.
- It mandates the use of PPE such as gloves, goggles, and helmets to minimize exposure to hazards.
- Make sure that all workspaces, including walking surfaces, storage areas, and manufacturing floors, are maintained hygienic, tidy, and orderly.
- Be sure that all potential hazards are removed from walking and working surfaces, such as sharp or protruding objects, loose floors, spills, chemical leaks, snow, and ice.
- Ensure that there are safe routes for workers to enter and depart walking-working zones.
Construction Industry Standards
Construction industry standards (29 CFR Part 1926) address the unique hazards found on construction sites. Important standards include:
- Requires protective measures for workers at heights to prevent falls, which are a leading cause of fatalities in construction.
- Sets requirements for the safe design and use of scaffolding to prevent falls and structural collapses.
- Specifies safety measures for trenching and excavation work to prevent cave-ins and other hazards.
- Addresses the safe installation and use of electrical systems on construction sites.
- Employers are required to implement practical administrative and engineering solutions in areas where sound levels are detrimental.
- Employers must make sure that workers have the availability of PPE that guards them from damaging sound levels and excessive noise exposure in the event that such measures are unsuccessful.
- Provide fall protection to workers at six feet or above, with things like guardrails, security nets, and safety ropes.
- For the course of any construction, repair, alteration, or demolition work, employers are in charge of creating and maintaining an efficient fire safety and prevention policy.
Maritime Industry Standards
Maritime industry standards (29 CFR Parts 1915, 1917, and 1918) focus on the hazards in shipbuilding, ship repair, and marine terminal operations. Key standards include:
- Covers safety and health requirements for shipbuilding, ship repair, and shipbreaking activities.
- Addresses the unique hazards of working in marine terminals, including cargo handling and storage.
- Focuses on safety practices for loading and unloading ships, including proper use of lifting equipment and protection against fall.
- Make sure that the words “Not Safe for Workers” are displayed in any room that has been found to be oxygen-enriched or oxygen-deficient.
- Ensure that every room and area has an oxygen concentration between 19.5 and 22.0 percent. Any room or area with an oxygen level that is not within the permitted range must be marked as “Not Safe for Workers.”
Agricultural Standards
Agricultural standards (29 CFR Part 1928) are tailored to the specific hazards in farming and related activities. Key standards include:
- Requires rollover protective structures (ROPS) on tractors to prevent fatalities in case of rollovers.
- Establishes guidelines for the safe handling and application of pesticides to protect workers from chemical exposure.
- Mandates access to clean drinking water, handwashing facilities, and toilets for agricultural workers.
- Sets restrictions on the types of work and hours that minors can work in agriculture to prevent exploitation and ensure safety.
- Provide free, hygienic drinking water to workers in the field: the water must be enough and suitably cold to meet the needs of every field worker.
How are OSHA Standards Developed and Updated?
OSHA standards are developed and updated through a comprehensive and participatory process that involves input from various stakeholders, including industry experts, employers, employees, and public health professionals.
However, this process begins with identifying the need for a new standard or an update to an existing one, often prompted by new research, technological advancements, or workplace incident data. OSHA then initiates a detailed review and consultation phase, which includes public hearings and comment periods to gather diverse perspectives and insights.
Identifying Hazards:
OSHA identifies emerging hazards through research, workplace inspections, and consultations with industry experts.
Stakeholder Input:
OSHA solicits input from employers, workers, trade associations, and health professionals through public meetings, hearings, and comment periods.
Rulemaking Process:
Draft standards are developed and published in the Federal Register, followed by a comment period where stakeholders can provide feedback.
Finalization and Implementation:
After reviewing comments and making necessary revisions, OSHA publishes the final standard, which becomes enforceable after a specified period.
adherence and Enforcement of OSHA Standards
If you do not adhere with OSHA safety standards, the OSHA is in charge of taking action against employers and organizations. So, here are some key points to know;
Inspections:
OSHA conducts inspections based on factors such as worker complaints, high-hazard industries, and follow-up on previous violations.
Penalties:
Employers found in violation of OSHA standards can face significant fines, which increase with the severity and frequency of the violations.
Consultation Programs:
OSHA offers free consultation services to help small and medium-sized businesses identify and correct hazards without the risk of penalties.
Training and Education:
OSHA provides training resources to help employers and workers understand and adhere with safety standards.
Impact of OSHA Standards on Workplace Safety
The implementation of OSHA standards has significantly improved workplace safety across the United States. The number of incidences of worker illnesses and injuries has decreased, from 10.9 per 100 employees in 1972 to 2.7 per one hundred employees in 2022.
Some notable impacts include:
- Reduction in Workplace Fatalities
- Decrease in Injury and Illness Rates
- Cost Savings, less downtime, and higher productivity.
- Cultural shift where workplace safety is prioritized
Final Verdict
OSHA regulations are essential for ensuring the health and safety of every worker. OSHA contributes to the reduction of occupational diseases, injuries, and fatalities by establishing and enforcing standards across a range of industries. The significant decline in occupational injuries and fatalities over the previous few decades highlights the significance and efficacy of OSHA’s mission.
Related Posts

360° Video Safety Training for High-Risk Construction

Workplace Safety Survey: What 500 U.S. Workers Revealed



